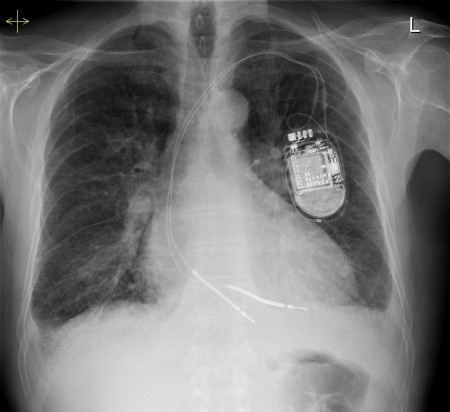
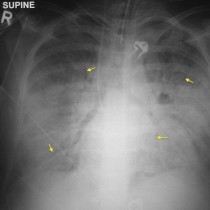
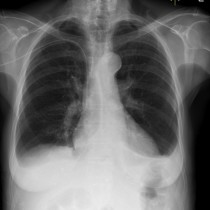
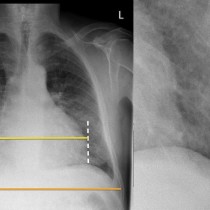
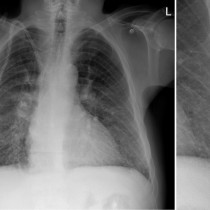
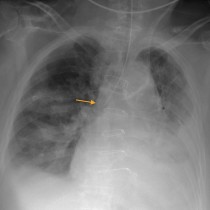
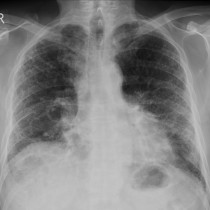
Pulmonary oedema – Kerley B lines
This is a nice example of heart failure – the heart is enlarged and there is a dual-chamber pacing device in situ. You will note that there are small bilateral pleural effusions, as well as dozens of Kerley B lines in the peripheries of both lungs.